The United States shares land borders with only two countries - Canada to the north and Mexico to the south. One of these borders is significantly longer than the other, with interesting geographical features and historical context that shaped these international boundaries.
When looking at a map of North America, you'll notice the United States shares land borders with just two countries: Canada to the north and Mexico to the south. A common question that arises is which of these borders is longer. The answer might seem obvious to some, but the actual numbers and the stories behind these boundaries contain fascinating geographical and historical elements worth exploring.
These international boundaries not only define the territorial limits of these nations but also represent complex political, economic, and cultural relationships that have evolved over centuries. Let's explore the lengths of these borders and what makes each unique.
Border Lengths Comparison: The Numbers
The answer to which border is longer is clear from the statistics: The US-Canada border is significantly longer than the US-Mexico border.
The US-Canada border stretches approximately 5,525 miles (8,891 kilometers), making it the longest international border in the world. In contrast, the US-Mexico border extends about 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers)-roughly one-third the length of the northern border.
This substantial difference exists because the US shares a much wider geographical connection with Canada, spanning the entire northern edge of the contiguous United States from Maine to Washington, plus the border between Alaska and Canada.
The US-Canada Border: The World's Longest International Border
The US-Canada border is not just longer than the US-Mexico border-it holds the distinction of being the longest international border between two countries in the world. This massive boundary includes:
- The mainland border between the contiguous US and Canada (approximately 3,987 miles/6,416 km)
- The Alaska-Canada border (approximately 1,538 miles/2,475 km)
- Numerous water boundaries through the Great Lakes and other bodies of water
A fascinating aspect of the US-Canada border is that a significant portion-approximately 40%-runs through water bodies, including the Great Lakes and various rivers. The land portion of the border consists of a 20-foot (6-meter) wide clearing that runs through forests, prairies, and mountainous regions.
The US-Mexico Border: Shorter But More Heavily Monitored
Although the US-Mexico border is significantly shorter at 1,954 miles, it is more heavily monitored and fortified than its northern counterpart. This border runs from the Pacific Ocean at Imperial Beach, California, to the Gulf of Mexico at the mouth of the Rio Grande in Texas.
The southern border crosses diverse terrain including:
- Urban areas like San Diego-Tijuana and El Paso-Ciudad Juárez
- Remote desert regions in Arizona and New Mexico
- The Rio Grande river, which forms the entire border between Texas and Mexico (approximately 1,254 miles/2,018 km)
Unlike the northern border, significant portions of the US-Mexico boundary feature physical barriers, including various types of fencing and walls that have been constructed over the decades.

Geographical Features of Both Borders
Both borders present unique geographical challenges and features that have influenced their development and management.
The US-Canada border crosses:
- The Great Lakes system, which contains about 20% of the world's fresh surface water
- The Rocky Mountains and other significant mountain ranges
- Remote wilderness areas, particularly in Alaska, Montana, and Maine
- The Point Roberts exclave in Washington State, accessible by land only through Canada
The US-Mexico border traverses:
- The Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts, among the most challenging terrain for both border enforcement and migrants
- The Rio Grande river, which creates natural challenges as it changes course over time
- Densely populated twin cities where urban areas exist on both sides of the border
- Rugged mountainous regions, particularly in California and New Mexico
Historical Context of the US Borders
The establishment of these borders has deep historical roots that continue to influence modern relations between these nations.
The US-Canada border was largely determined by:
- The Treaty of Paris (1783) following the American Revolutionary War
- The Treaty of 1818, which established the 49th parallel as the boundary west of the Great Lakes
- The Oregon Treaty (1846), extending the 49th parallel boundary to the Pacific Ocean
- The purchase of Alaska from Russia in 1867, which added the Alaska-Canada border
The US-Mexico border was established through:
- The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) following the Mexican-American War, when Mexico ceded nearly half its territory to the US
- The Gadsden Purchase (1853), when the US acquired additional land in present-day Arizona and New Mexico
These historical agreements have created what is often described as the world's longest peaceful international boundary (US-Canada) and one of the world's most frequently crossed borders (US-Mexico).
Major Border Crossings and Ports of Entry
Despite their difference in length, both borders feature busy crossing points that facilitate massive trade and travel between the countries.
Major US-Canada crossings include:
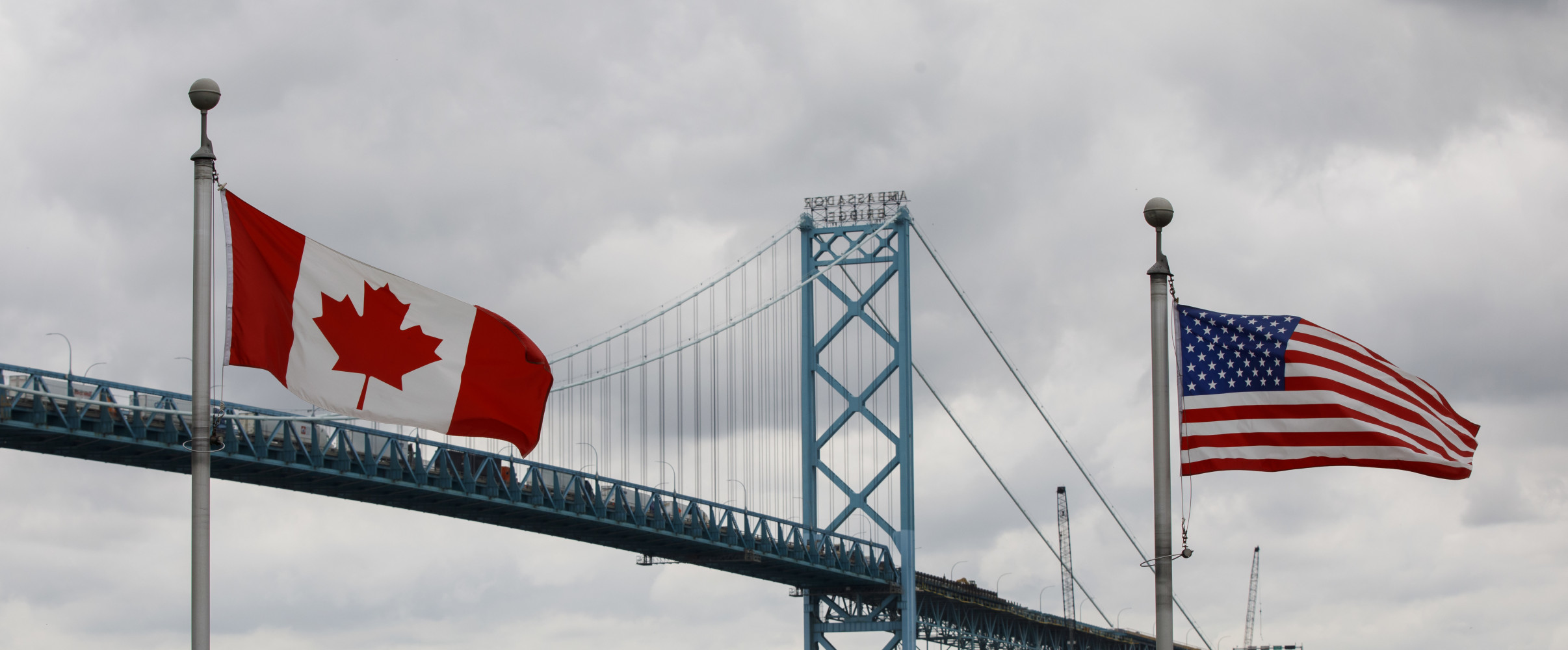
- Ambassador Bridge (Detroit-Windsor) - handling over $100 billion in annual trade
- Peace Bridge (Buffalo-Fort Erie)
- Blaine-Surrey crossing in the Pacific Northwest
Prominent US-Mexico crossings include:
- San Ysidro (San Diego-Tijuana) - the busiest land border crossing in the Western Hemisphere
- El Paso-Ciudad Juárez crossing
- Laredo-Nuevo Laredo - a major commercial transport hub
In total, there are over 100 official ports of entry along these two borders, facilitating billions of dollars in daily commerce and millions of legal crossings each year.

Frequently Asked Questions About Canada vs Mexico: Which U.S. Border Is Longer? (The Answer Might Surprise You)
How much longer is the US-Canada border than the US-Mexico border?
The US-Canada border is about 2.8 times longer than the US-Mexico border. The northern border measures approximately 5,525 miles (8,891 kilometers), while the southern border with Mexico extends about 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers).
Why is the US-Canada border so much longer?
The US-Canada border is longer because it spans the entire northern edge of the contiguous United States from the Atlantic to the Pacific, plus includes the extensive border between Alaska and Canada. The geographical connection between the US and Canada covers a much wider area than the US-Mexico border.
What percentage of the US-Canada border is water?
Approximately 40% of the US-Canada border runs through water, including the Great Lakes system and various rivers. This water boundary represents a significant portion of the world's longest international border.
Which US-Mexico border state has the longest boundary with Mexico?
Texas has the longest boundary with Mexico, stretching approximately 1,254 miles (2,018 kilometers) along the Rio Grande river. This represents about 64% of the entire US-Mexico border.
Is the entire US-Mexico border fenced or walled?
No, not the entire border has physical barriers. As of 2023, approximately 700 miles (1,125 kilometers) of the 1,954-mile US-Mexico border has some form of fencing, wall, or barrier. The remaining sections include natural barriers like rivers, mountains, and remote desert terrain.
What is the busiest border crossing between the US and Canada?
The Ambassador Bridge connecting Detroit, Michigan with Windsor, Ontario is the busiest US-Canada border crossing in terms of trade value, handling over $100 billion in annual commerce. It's a crucial link in the North American automotive supply chain.