The American landscape is shifting as millions of people relocate across state lines, creating new population centers and transforming economies. From sun-soaked southern states to mountain west boomtowns, these rapidly growing regions are reshaping the nation's demographic future.
America's population landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation as millions of residents pack up and relocate across state lines. This mass migration is reshaping the nation's demographic makeup, with certain states experiencing explosive growth while others face stagnation or decline. Understanding which states are growing fastest provides valuable insight into changing American preferences and economic opportunities.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated existing migration patterns, with many Americans prioritizing space, affordability, and quality of life over traditional urban amenities. Remote work opportunities have liberated many from location constraints, allowing for relocations based on lifestyle preferences rather than job proximity.
Population Growth Trends in the United States
The United States population continues to grow, but that growth is distributed unevenly. While the national population increased by roughly 0.4% between 2021 and 2022, some states are growing at rates three to four times faster than the national average.
Growth rates are influenced by three main factors: natural increase (births minus deaths), domestic migration (movement between states), and international migration. The fastest-growing states typically excel in at least two of these categories, with domestic migration currently playing the most significant role in rapid state growth.
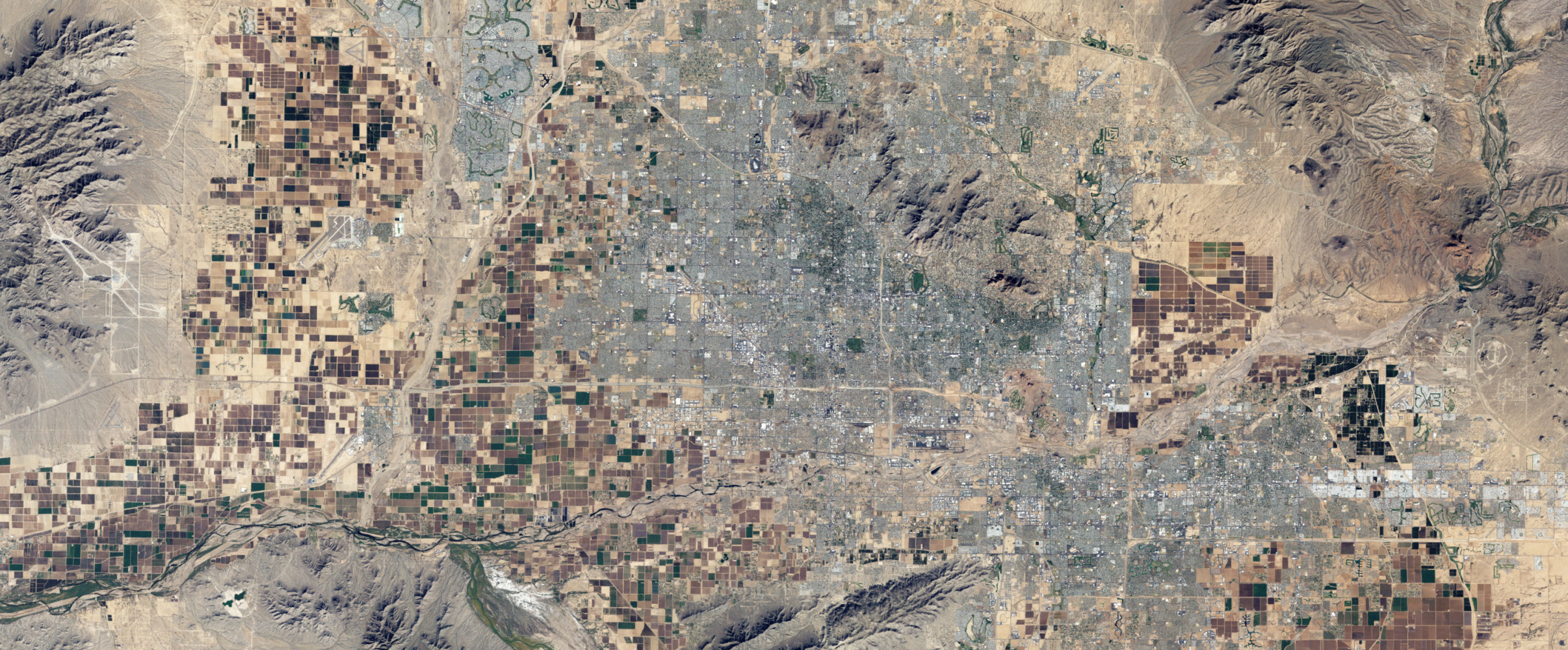
The geographic distribution of growth has shifted notably in recent years. The long-standing trend of Americans moving to coastal areas has given way to strong growth in the Mountain West, Southeast, and parts of the Southwest. Meanwhile, many Northeastern and Midwestern states have experienced minimal growth or population losses.
The Top 10 Fastest-Growing States
Based on recent Census Bureau data, these states are experiencing the most rapid population growth:
- Idaho: With growth rates consistently above 2% annually, Idaho leads the nation in percentage population increase. The Boise metropolitan area has become a magnet for transplants from California and Washington seeking lower costs of living.
- Texas: The Lone Star State continues its decades-long growth streak, adding more total residents than any other state. Major metropolitan areas like Austin, Dallas, and Houston are driving this expansion.
- Florida: Pandemic-era remote work accelerated Florida's already strong population growth, with the state adding over 400,000 new residents in a recent year alone.
- Utah: A combination of high birth rates and strong domestic migration keeps Utah near the top of fastest-growing states.
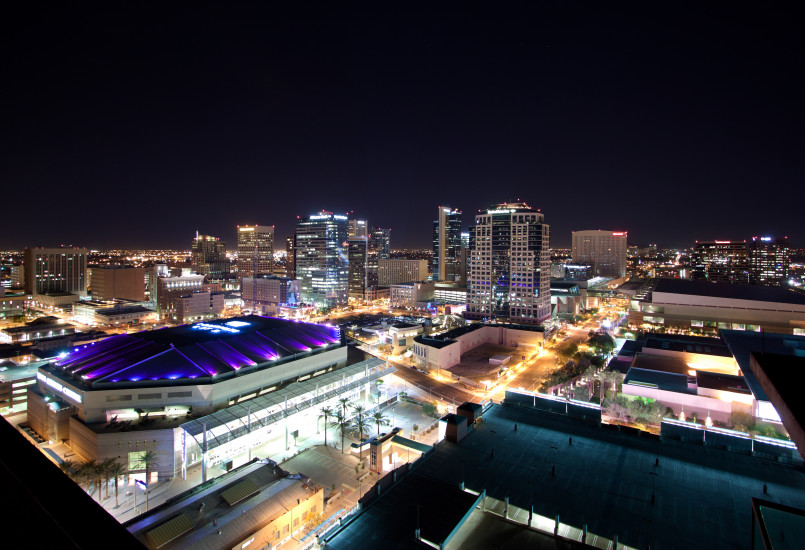
- Arizona: Retirement communities and growing technology sectors are fueling Arizona's rapid expansion, particularly in the Phoenix and Tucson areas.
- Nevada: Despite water concerns, Nevada continues to attract new residents with its combination of job opportunities and absence of state income tax.
- South Carolina: Coastal beauty, lower taxes, and a more relaxed lifestyle are drawing retirees and remote workers to the Palmetto State.
- Montana: Once sparsely populated, Montana is experiencing a boom as Americans seek outdoor amenities and natural beauty.
- Delaware: This small state has become increasingly attractive for its proximity to major Northeast cities combined with lower taxes and housing costs.
- North Carolina: Strong job growth in the Research Triangle and Charlotte metro areas continues to draw domestic migrants from across the country.

Why People Are Relocating: Key Factors Driving Growth
Several key factors are driving Americans to relocate to the fastest-growing states:
Housing affordability remains perhaps the most significant factor. As housing costs in coastal metropolitan areas like San Francisco, Los Angeles, New York, and Boston reach unsustainable levels for many residents, more affordable markets in the Southeast and Mountain West become increasingly attractive.
The rise of remote work has been transformative, with many knowledge workers now able to choose their location based on quality of life rather than proximity to an office. States offering outdoor recreation, pleasant weather, and lower costs of living have benefited tremendously from this shift.
Tax policy plays a significant role as well. States with no income tax, including Texas, Florida, Nevada, and Tennessee, have seen strong domestic migration, particularly among high-income earners from high-tax states.
Other factors include:
- Job opportunities in growing sectors
- Weather and climate preferences
- Proximity to outdoor recreation
- Lower regulatory burdens for businesses
- Political preferences
- Family connections
Economic Impact of Rapid Population Growth
The economic implications of rapid population growth are profound and multifaceted. For fast-growing states, the influx of new residents typically brings significant economic benefits, including expanded tax bases, increased consumer spending, and new business formation.
Many fast-growing states are experiencing virtuous economic cycles where population growth leads to business expansion, which creates more jobs and attracts more residents. Texas exemplifies this pattern, with its population boom corresponding with strong employment growth and business relocations from other states.
However, rapid growth also presents challenges. Labor markets can become tight, driving up wages and creating hiring difficulties for employers. Local businesses may struggle to scale quickly enough to meet increased demand.
For states losing population, the economic impacts can be concerning. Shrinking tax bases may make it difficult to maintain infrastructure and services, potentially creating downward spirals where declining quality of life accelerates outmigration.
Housing and Infrastructure Challenges
The fastest-growing states face significant challenges in accommodating their expanding populations. Housing shortages have become acute in many high-growth areas, with construction unable to keep pace with demand.
Idaho, Utah, and Arizona have seen some of the nation's fastest home price appreciation as their housing markets struggle to absorb newcomers. In Boise, median home prices increased by over 70% in just three years, creating affordability challenges for long-time residents.

Infrastructure systems face similar strains. Transportation networks designed for smaller populations become congested, water systems reach capacity limits, and schools become overcrowded. States like Texas and Florida are racing to expand their infrastructure, but funding and building these systems takes time.
Some fast-growing regions also face environmental constraints. Water scarcity in the Southwest raises questions about the sustainability of continued rapid growth in states like Arizona and Nevada. Meanwhile, development pressure threatens natural areas and wildlife habitats throughout the Mountain West.
Future Growth Projections
Population experts expect current growth trends to continue for the foreseeable future, though perhaps at a somewhat moderated pace as pandemic-driven migration settles. The Census Bureau projects that the South and West will continue to gain population share at the expense of the Northeast and Midwest.
Several factors may influence future growth patterns:
Climate change considerations could begin to affect migration patterns, potentially slowing growth in areas facing increased drought, wildfire risk, or hurricane exposure.
The evolution of remote work policies will be crucial. If companies maintain flexible work arrangements, geographic distribution will likely continue to spread. If there's a significant return-to-office movement, growth may reconcentrate around major employment centers.
Housing affordability challenges in currently fast-growing areas may eventually dampen their appeal. Places like Boise and Austin have seen such rapid price appreciation that they've lost some of their cost advantages compared to the places migrants are leaving.
Ultimately, America's population will likely continue its long-term shift toward the Sun Belt and Mountain West, though the specific states seeing the most rapid growth may evolve over time as economic conditions and lifestyle preferences change.
Frequently Asked Questions About 10 Fastest-Growing States in America: Where Population is Booming in 2023
Which state has added the most total residents in recent years?
While Idaho leads in percentage growth, Texas has added the most total residents in recent years. The Lone Star State consistently adds hundreds of thousands of new residents annually through both domestic migration and natural increase (births exceeding deaths).
Are people mainly moving to cities or rural areas in these growing states?
The growth patterns show a mixed picture. Metropolitan areas in growing states are generally seeing the strongest population increases, especially in their suburban rings. However, some rural areas with natural amenities and outdoor recreation opportunities are also experiencing significant growth, particularly as remote work becomes more common.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected migration patterns?
The pandemic accelerated existing migration trends, with more people leaving high-cost urban areas for more affordable regions. Remote work opportunities freed many knowledge workers from location constraints, allowing them to prioritize quality of life and housing affordability over proximity to offices.
What impact does rapid growth have on existing residents of these states?
The effects are mixed. Growth typically brings economic benefits including job opportunities, rising home values, and expanded amenities. However, it can also lead to housing affordability challenges, traffic congestion, strained public services, and changes to community character that some long-term residents find concerning.
Are any Northeast or Midwest states experiencing significant growth?
While the fastest growth is concentrated in the South and West, some Northeast and Midwest states are seeing pockets of growth. Delaware is growing rapidly despite its Northeast location. Also, certain metropolitan areas like Columbus, Ohio and Indianapolis, Indiana are growing even as their states overall see modest population changes.
How are water resources affecting growth patterns?
Water availability is becoming an increasingly important constraint on growth, particularly in the Southwest. States like Arizona and Nevada face significant long-term water challenges that could eventually limit their capacity for continued rapid population growth. Some water-stressed communities have begun implementing growth restrictions or conservation requirements for new development.






